Top things web developers should know about the Visual Studio 2013 release
Posted
by Jon Galloway
on ASP.net Weblogs
See other posts from ASP.net Weblogs
or by Jon Galloway
Published on Thu, 17 Oct 2013 21:36:03 GMT
Indexed on
2013/10/17
21:55 UTC
Read the original article
Hit count: 1350
ASP.NET and Web Tools for Visual Studio 2013 Release NotesASP.NET and Web Tools for Visual Studio 2013 Release NotesSummary for lazy readers:
- Visual Studio 2013 is now available for download on the Visual Studio site and on MSDN subscriber downloads)
- Visual Studio 2013 installs side by side with Visual Studio 2012 and supports round-tripping between Visual Studio versions, so you can try it out without committing to a switch
- Visual Studio 2013 ships with the new version of ASP.NET, which includes ASP.NET MVC 5, ASP.NET Web API 2, Razor 3, Entity Framework 6 and SignalR 2.0
- The new releases ASP.NET focuses on One ASP.NET, so core features and web tools work the same across the platform (e.g. adding ASP.NET MVC controllers to a Web Forms application)
- New core features include new templates based on Bootstrap, a new scaffolding system, and a new identity system
- Visual Studio 2013 is an incredible editor for web files, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Markdown, LESS, Coffeescript, Handlebars, Angular, Ember, Knockdown, etc.
Top links:
- Visual Studio 2013 content on the ASP.NET site are in the standard new releases area: http://www.asp.net/vnext
- ASP.NET and Web Tools for Visual Studio 2013 Release Notes
- Short intro videos on the new Visual Studio web editor features from Scott Hanselman and Mads Kristensen
- Announcing release of ASP.NET and Web Tools for Visual Studio 2013 post on the official .NET Web Development and Tools Blog
- Scott Guthrie's post: Announcing the Release of Visual Studio 2013 and Great Improvements to ASP.NET and Entity Framework
Okay, for those of you who are still with me, let's dig in a bit.
Quick web dev notes on downloading and installing Visual Studio 2013
I found Visual Studio 2013 to be a pretty fast install. According to Brian Harry's release post, installing over pre-release versions of Visual Studio is supported. I've installed the release version over pre-release versions, and it worked fine.
If you're only going to be doing web development, you can speed up the install if you just select Web Developer tools.
Of course, as a good Microsoft employee, I'll mention that you might also want to install some of those other features, like the Store apps for Windows 8 and the Windows Phone 8.0 SDK, but they do download and install a lot of other stuff (e.g. the Windows Phone SDK sets up Hyper-V and downloads several GB's of VM's). So if you're planning just to do web development for now, you can pick just the Web Developer Tools and install the other stuff later.
If you've got a fast internet connection, I recommend using the web installer instead of downloading the ISO. The ISO includes all the features, whereas the web installer just downloads what you're installing.
Visual Studio 2013 development settings and color theme
When you start up Visual Studio, it'll prompt you to pick some defaults. These are totally up to you -whatever suits your development style - and you can change them later.
As I said, these are completely up to you. I recommend either the Web Development or Web Development (Code Only) settings. The only real difference is that Code Only hides the toolbars, and you can switch between them using Tools / Import and Export Settings / Reset.
Web Development settings
Web Development (code only) settings
Usually I've just gone with Web Development (code only) in the past because I just want to focus on the code, although the Standard toolbar does make it easier to switch default web browsers. More on that later.
Color theme
Sigh. Okay, everyone's got their favorite colors. I alternate between Light and Dark depending on my mood, and I personally like how the low contrast on the window chrome in those themes puts the emphasis on my code rather than the tabs and toolbars. I know some people got pretty worked up over that, though, and wanted the blue theme back. I personally don't like it - it reminds me of ancient versions of Visual Studio that I don't want to think about anymore.
So here's the thing: if you install Visual Studio Ultimate, it defaults to Blue. The other versions default to Light. If you use Blue, I won't criticize you - out loud, that is. You can change themes really easily - either Tools / Options / Environment / General, or the smart way: ctrl+q for quick launch, then type Theme and hit enter.
Signing in
During the first run, you'll be prompted to sign in. You don't have to - you can click the "Not now, maybe later" link at the bottom of that dialog. I recommend signing in, though. It's not hooked in with licensing or tracking the kind of code you write to sell you components. It is doing good things, like syncing your Visual Studio settings between computers. More about that here. So, you don't have to, but I sure do.
Overview of shiny new things in ASP.NET land
There are a lot of good new things in ASP.NET. I'll list some of my favorite here, but you can read more on the ASP.NET site.
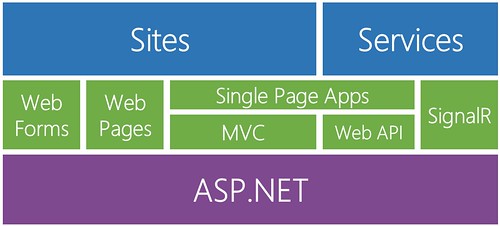
One ASP.NET
You've heard us talk about this for a while. The idea is that options are good, but choice can be a burden. When you start a new ASP.NET project, why should you have to make a tough decision - with long-term consequences - about how your application will work? If you want to use ASP.NET Web Forms, but have the option of adding in ASP.NET MVC later, why should that be hard? It's all ASP.NET, right?
Ideally, you'd just decide that you want to use ASP.NET to build sites and services, and you could use the appropriate tools (the green blocks below) as you needed them.
So, here it is.
When you create a new ASP.NET application, you just create an ASP.NET application.
Next, you can pick from some templates to get you started... but these are different. They're not "painful decision" templates, they're just some starting pieces. And, most importantly, you can mix and match. I can pick a "mostly" Web Forms template, but include MVC and Web API folders and core references.
If you've tried to mix and match in the past, you're probably aware that it was possible, but not pleasant. ASP.NET MVC project files contained special project type GUIDs, so you'd only get controller scaffolding support in a Web Forms project if you manually edited the csproj file. Features in one stack didn't work in others. Project templates were painful choices. That's no longer the case. Hooray!
I just did a demo in a presentation last week where I created a new Web Forms + MVC + Web API site, built a model, scaffolded MVC and Web API controllers with EF Code First, add data in the MVC view, viewed it in Web API, then added a GridView to the Web Forms Default.aspx page and bound it to the Model. In about 5 minutes. Sure, it's a simple example, but it's great to be able to share code and features across the whole ASP.NET family.
Authentication
In the past, authentication was built into the templates. So, for instance, there was an ASP.NET MVC 4 Intranet Project template which created a new ASP.NET MVC 4 application that was preconfigured for Windows Authentication. All of that authentication stuff was built into each template, so they varied between the stacks, and you couldn't reuse them. You didn't see a lot of changes to the authentication options, since they required big changes to a bunch of project templates.
Now, the new project dialog includes a common authentication experience. When you hit the Change Authentication button, you get some common options that work the same way regardless of the template or reference settings you've made. These options work on all ASP.NET frameworks, and all hosting environments (IIS, IIS Express, or OWIN for self-host)
The default is Individual User Accounts:
This is the standard "create a local account, using username / password or OAuth" thing; however, it's all built on the new Identity system. More on that in a second.
The one setting that has some configuration to it is Organizational Accounts, which lets you configure authentication using Active Directory, Windows Azure Active Directory, or Office 365.
Identity
There's a new identity system. We've taken the best parts of the previous ASP.NET Membership and Simple Identity systems, rolled in a lot of feedback and made big enhancements to support important developer concerns like unit testing and extensiblity.
I've written long posts about ASP.NET identity, and I'll do it again. Soon. This is not that post. The short version is that I think we've finally got just the right Identity system. Some of my favorite features:
- There are simple, sensible defaults that work well - you can File / New / Run / Register / Login, and everything works.
- It supports standard username / password as well as external authentication (OAuth, etc.).
- It's easy to customize without having to re-implement an entire provider. It's built using pluggable pieces, rather than one large monolithic system.
- It's built using interfaces like IUser and IRole that allow for unit testing, dependency injection, etc.
- You can easily add user profile data (e.g. URL, twitter handle, birthday). You just add properties to your ApplicationUser model and they'll automatically be persisted.
- Complete control over how the identity data is persisted. By default, everything works with Entity Framework Code First, but it's built to support changes from small (modify the schema) to big (use another ORM, store your data in a document database or in the cloud or in XML or in the EXIF data of your desktop background or whatever).
- It's configured via OWIN. More on OWIN and Katana later, but the fact that it's built using OWIN means it's portable.
You can find out more in the Authentication and Identity section of the ASP.NET site (and lots more content will be going up there soon).
New Bootstrap based project templates
The new project templates are built using Bootstrap 3. Bootstrap (formerly Twitter Bootstrap) is a front-end framework that brings a lot of nice benefits:
- It's responsive, so your projects will automatically scale to device width using CSS media queries. For example, menus are full size on a desktop browser, but on narrower screens you automatically get a mobile-friendly menu.
- The built-in Bootstrap styles make your standard page elements (headers, footers, buttons, form inputs, tables etc.) look nice and modern.
- Bootstrap is themeable, so you can reskin your whole site by dropping in a new Bootstrap theme. Since Bootstrap is pretty popular across the web development community, this gives you a large and rapidly growing variety of templates (free and paid) to choose from.
- Bootstrap also includes a lot of very useful things: components (like progress bars and badges), useful glyphicons, and some jQuery plugins for tooltips, dropdowns, carousels, etc.).
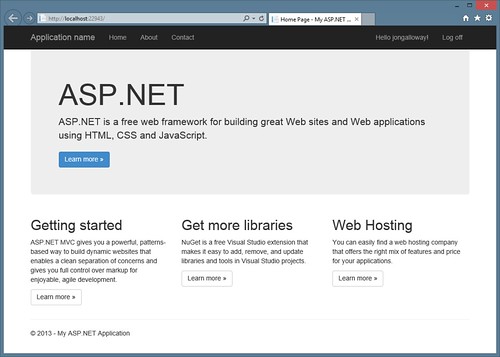
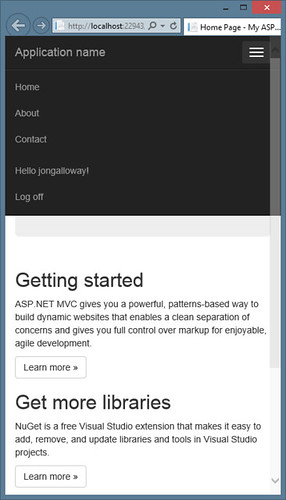
Here's a look at how the responsive part works. When the page is full screen, the menu and header are optimized for a wide screen display:
When I shrink the page down (this is all based on page width, not useragent sniffing) the menu turns into a nice mobile-friendly dropdown:
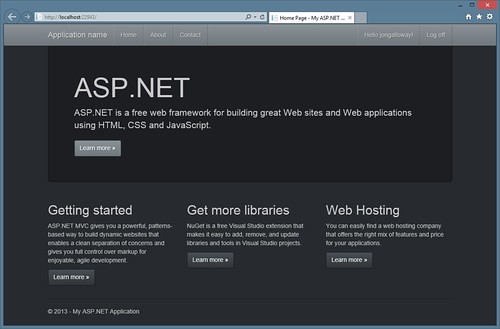
For a quick example, I grabbed a new free theme off bootswatch.com. For simple themes, you just need to download the boostrap.css file and replace the /content/bootstrap.css file in your project.
Now when I refresh the page, I've got a new theme:
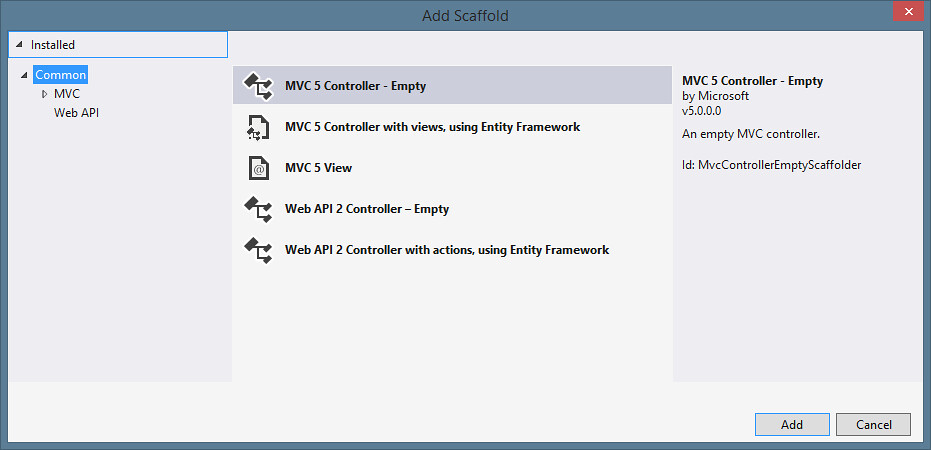
Scaffolding
The big change in scaffolding is that it's one system that works across ASP.NET. You can create a new Empty Web project or Web Forms project and you'll get the Scaffold context menus.
For release, we've got MVC 5 and Web API 2 controllers. We had a preview of Web Forms scaffolding in the preview releases, but they weren't fully baked for RTM. Look for them in a future update, expected pretty soon.
This scaffolding system wasn't just changed to work across the ASP.NET frameworks, it's also built to enable future extensibility. That's not in this release, but should also hopefully be out soon.
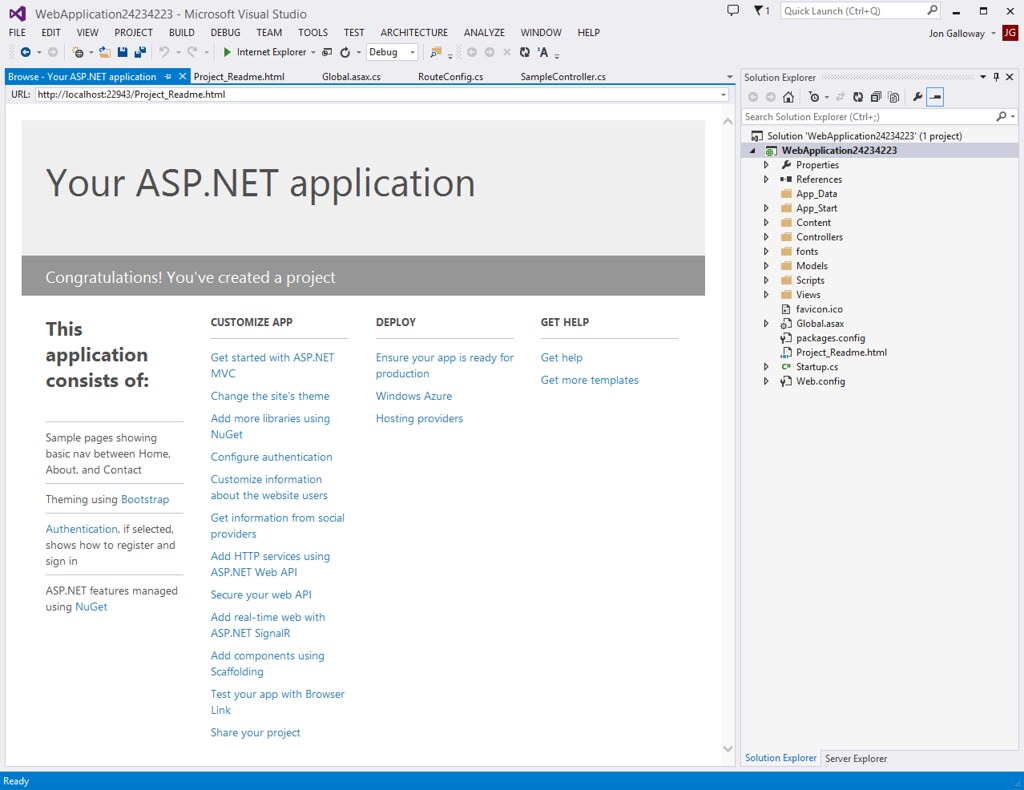
Project Readme page
This is a small thing, but I really like it. When you create a new project, you get a Project_Readme.html page that's added to the root of your project and opens in the Visual Studio built-in browser.
I love it.
A long time ago, when you created a new project we just dumped it on you and left you scratching your head about what to do next. Not ideal.
Then we started adding a bunch of Getting Started information to the new project templates. That told you what to do next, but you had to delete all of that stuff out of your website. It doesn't belong there. Not ideal.
This is a simple HTML file that's not integrated into your project code at all. You can delete it if you want. But, it shows a lot of helpful links that are current for the project you just created. In the future, if we add new wacky project types, they can create readme docs with specific information on how to do appropriately wacky things.
Side note: I really like that they used the internal browser in Visual Studio to show this content rather than popping open an HTML page in the default browser. I hate that. It's annoying. If you're doing that, I hope you'll stop. What if some unnamed person has 40 or 90 tabs saved in their browser session? When you pop open your "Thanks for installing my Visual Studio extension!" page, all eleventy billion tabs start up and I wish I'd never installed your thing. Be like these guys and pop stuff Visual Studio specific HTML docs in the Visual Studio browser.
ASP.NET MVC 5
The biggest change with ASP.NET MVC 5 is that it's no longer a separate project type. It integrates well with the rest of ASP.NET.
In addition to that and the other common features we've already looked at (Bootstrap templates, Identity, authentication), here's what's new for ASP.NET MVC.
Attribute routing
ASP.NET MVC now supports attribute routing, thanks to a contribution by Tim McCall, the author of http://attributerouting.net. With attribute routing you can specify your routes by annotating your actions and controllers. This supports some pretty complex, customized routing scenarios, and it allows you to keep your route information right with your controller actions if you'd like.
Here's a controller that includes an action whose method name is Hiding, but I've used AttributeRouting to configure it to /spaghetti/with-nesting/where-is-waldo
public class SampleController : Controller
{
[Route("spaghetti/with-nesting/where-is-waldo")]
public string Hiding()
{
return "You found me!";
}
}
I enable that in my RouteConfig.cs, and I can use that in conjunction with my other MVC routes like this:
public class RouteConfig
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapMvcAttributeRoutes();
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
You can read more about Attribute Routing in ASP.NET MVC 5 here.
Filter enhancements
There are two new additions to filters: Authentication Filters and Filter Overrides.
Authentication filters are a new kind of filter in ASP.NET MVC that run prior to authorization filters in the ASP.NET MVC pipeline and allow you to specify authentication logic per-action, per-controller, or globally for all controllers. Authentication filters process credentials in the request and provide a corresponding principal. Authentication filters can also add authentication challenges in response to unauthorized requests.
Override filters let you change which filters apply to a given action method or controller. Override filters specify a set of filter types that should not be run for a given scope (action or controller). This allows you to configure filters that apply globally but then exclude certain global filters from applying to specific actions or controllers.
ASP.NET Web API 2
ASP.NET Web API 2 includes a lot of new features.
Attribute Routing
ASP.NET Web API supports the same attribute routing system that's in ASP.NET MVC 5. You can read more about the Attribute Routing features in Web API in this article.
OAuth 2.0
ASP.NET Web API picks up OAuth 2.0 support, using security middleware running on OWIN (discussed below). This is great for features like authenticated Single Page Applications.
OData Improvements
ASP.NET Web API now has full OData support. That required adding in some of the most powerful operators: $select, $expand, $batch and $value. You can read more about OData operator support in this article by Mike Wasson.
Lots more
There's a huge list of other features, including CORS (cross-origin request sharing), IHttpActionResult, IHttpRequestContext, and more. I think the best overview is in the release notes.
OWIN and Katana
I've written about OWIN and Katana recently. I'm a big fan.
OWIN is the Open Web Interfaces for .NET. It's a spec, like HTML or HTTP, so you can't install OWIN. The benefit of OWIN is that it's a community specification, so anyone who implements it can plug into the ASP.NET stack, either as middleware or as a host.
Katana is the Microsoft implementation of OWIN. It leverages OWIN to wire up things like authentication, handlers, modules, IIS hosting, etc., so ASP.NET can host OWIN components and Katana components can run in someone else's OWIN implementation.
Howard Dierking just wrote a cool article in MSDN magazine describing Katana in depth: Getting Started with the Katana Project. He had an interesting example showing an OWIN based pipeline which leveraged SignalR, ASP.NET Web API and NancyFx components in the same stack.
.png)
If this kind of thing makes sense to you, that's great. If it doesn't, don't worry, but keep an eye on it. You're going to see some cool things happen as a result of ASP.NET becoming more and more pluggable.
Visual Studio Web Tools
Okay, this stuff's just crazy. Visual Studio has been adding some nice web dev features over the past few years, but they've really cranked it up for this release.
Visual Studio is by far my favorite code editor for all web files: CSS, HTML, JavaScript, and lots of popular libraries.
Stop thinking of Visual Studio as a big editor that you only use to write back-end code. Stop editing HTML and CSS in Notepad (or Sublime, Notepad++, etc.). Visual Studio starts up in under 2 seconds on a modern computer with an SSD. Misspelling HTML attributes or your CSS classes or jQuery or Angular syntax is stupid. It doesn't make you a better developer, it makes you a silly person who wastes time.
Browser Link
Browser Link is a real-time, two-way connection between Visual Studio and all connected browsers. It's only attached when you're running locally, in debug, but it applies to any and all connected browser, including emulators.
You may have seen demos that showed the browsers refreshing based on changes in the editor, and I'll agree that's pretty cool. But it's really just the start. It's a two-way connection, and it's built for extensiblity. That means you can write extensions that push information from your running application (in IE, Chrome, a mobile emulator, etc.) back to Visual Studio. Mads and team have showed off some demonstrations where they enabled edit mode in the browser which updated the source HTML back on the browser. It's also possible to look at how the rendered HTML performs, check for compatibility issues, watch for unused CSS classes, the sky's the limit.
New HTML editor
The previous HTML editor had a lot of old code that didn't allow for improvements. The team rewrote the HTML editor to take advantage of the new(ish) extensibility features in Visual Studio, which then allowed them to add in all kinds of features - things like CSS Class and ID IntelliSense (so you type style="" and get a list of classes and ID's for your project), smart indent based on how your document is formatted, JavaScript reference auto-sync, etc.
Here's a 3 minute tour from Mads Kristensen.
The previous HTML editor had a lot of old code that didn't allow for improvements. The team rewrote the HTML editor to take advantage of the new(ish) extensibility features in Visual Studio, which then allowed them to add in all kinds of features - things like CSS Class and ID IntelliSense (so you type style="" and get a list of classes and ID's for your project), smart indent based on how your document is formatted, JavaScript reference auto-sync, etc.
Lots more Visual Studio web dev features
That's just a sampling - there's a ton of great features for JavaScript editing, CSS editing, publishing, and Page Inspector (which shows real-time rendering of your page inside Visual Studio). Here are some more short videos showing those features.
Lots, lots more
Okay, that's just a summary, and it's still quite a bit. Head on over to http://asp.net/vnext for more information, and download Visual Studio 2013 now to get started!
© ASP.net Weblogs or respective owner